 Alysse Merila
Alysse Merila
 Henrik Lang
Henrik Lang
 Megan Sandquist
Megan Sandquist
Background
With the 2026 proxy season on the horizon, Compensation Committees are reassessing their equity plan strategies and shareholder engagement priorities. Equity plans are essential to funding equity compensation programs, which generally comprise the largest portion of executive compensation. Given recent share price pressure in select industries (e.g., retail), many companies have had to return to shareholders to request shares more frequently or have had to go above the norm in terms of the number of shares to request. In this article, Meridian describes how Institutional Shareholder Services (ISS), a major proxy advisory firm, evaluates equity plan proposals, examines strategies for companies to garner shareholder support in instances where ISS initially opposes their proposals, and explores institutional investor outlook on equity plans.
How Does ISS Evaluate Equity Plans?
ISS evaluates equity program proposals under the Equity Plan Scorecard (EPSC) policy. This framework assesses multiple factors under three pillars: plan cost, plan features, and grant practices. Each factor carries a maximum potential weighting, culminating in a total score out of 100 points. This score typically determines whether ISS recommends “For” or “Against” for the plan. A company’s equity plan must exceed a threshold score to receive ISS support.
Success of Shareholder Proposals
While ISS recommendations can influence shareholder voting behaviors, ISS support is not essential to ensuring that an equity plan receives majority support from a company’s shareholders. In fact, depending on the circumstance, a company may need to request shares beyond what the ISS model would permit to have sufficient shares for annual equity awards. The following are key findings from our review of equity proposals in the S&P 500 and Russell 3000 Consumer Discretionary sector from January 1, 2023 to present:
• Nearly all equity plan proposals pass (99.6%)
• On average, approximately 78.9% of S&P 500 Consumer Discretionary proposals received ISS support; within the Russell 3000 Consumer Discretionary industry, ISS support is slightly lower at 67.6%.
― Common reasons that companies do not receive ISS support include the following:
• Limited availability of new shares (e.g., not enough to cover the annual award) under the ISS model due to large existing overhang or low current share price
• Problematic plan design features including liberal share recycling, single trigger change-in-control, and evergreen provisions
• Excessive dilution or grant practices relative to ISS benchmarks
• Insufficient minimum vesting period (generally less than one year)
• While a negative ISS vote recommendation may materially depress FOR votes, it rarely results in the failure of an equity plan proposal
• 94.2% of equity plan proposals that receive an ISS “against” vote recommendation ultimately pass (50% of votes plus 1) but may require additional shareholder outreach efforts
Over the past three years, vast majority of proposals received ISS support. On average, approximately 73.2% of proposals received ISS support among both the Russell 3000 and S&P 500.
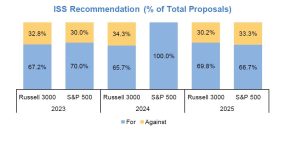
During the past 3 years, there has been an average difference of 18.5 percentage points in shareholder votes between equity plan proposals that received ISS support and those that did not.
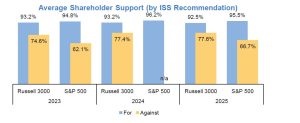
Among all the equity plan proposals in the consumer discretionary industry in the past three years, only one proposal has failed.
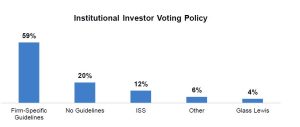
Institutional Investors Policy on Voting for Equity Incentive Plans
When seeking support for equity incentive plans, a company should consider the vote policies of its major institutional investors, including whether each institutional investor has published guidelines, follows or considers the vote recommendations of ISS and/or Glass Lewis, and has dilution or burn rate limits. Some institutional investors will assess dilution and burn rate in the context of the company’s industry, business needs, and executive pay programs.
Achieve Successful Voting Outcomes
Crafting a roadmap to achieve success in the absence of anticipated ISS support requires a holistic approach. Meridian recommends the following roadmap to increase the likelihood of a successful voting outcome among shareholders.
• Conduct a thorough analysis of equity burn rate to understand historical share practices and how dilutive recent grants have been as well as compare these grant practices against industry peers.
• Review ISS’s EPSC evaluation criteria to address ISS concerns and make appropriate plan design changes.
• Coordinate with the Board committee to ensure alignment on equity plan features and decision-making.
• Engage in targeted shareholder outreach to rally shareholder support.
Note: 2025 results are through December 8, 2025
